The ACT@Scale project responds to the need for a deeper look into the results and conclusions that came out of the previous project, Advancing Care Coordination and Telehealth Deployment (2013-2015) and it follows the strategic lines proposed by the European Association on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA).
This new project, ACT@Scale, began in March 2016 within the framework of the Horizon 2020 programme which was financed by the European Union. The aim is on transforming health processes and the provision of services related to integrated care and telemonitoring.

How have we done all this?
Different regions in Europe, the industry and innovative academic institutions have worked in collaboration over these past few years. The Agency for Health Quality and Assessment of Catalonia (AQuAS) has been one of the partners in this consortium leading the work-package Change Management, Stakeholder Management and Staff Engagement.
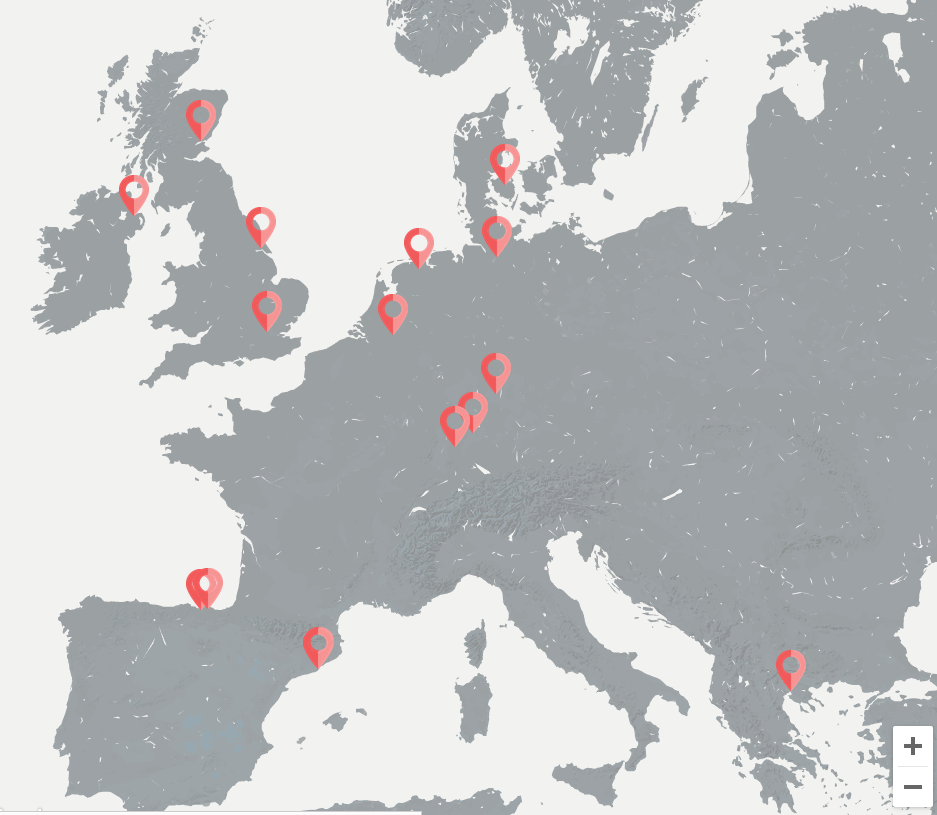
With 15 partners, in association, from 8 countries of the European Union and with the coordination of Phillips Healthcare we have worked collaboratively in order to consolidate and scale up the best practices identified in integrated care and telemonitoring so that they can be transferred to other European regions.
The Basque Country, The Netherlands, Scotland, Germany and Catalonia have contributed with a total of 15 programmes of integrated care, both innovative and of reference, regarding best practices in health. In particular, Catalonia has participated with five reference programmes of good practices in integrated care: Programme of Chronic Care, of the Badalona Serveis Assistencials; Nursing Homes, of MUTUAM; Frail Care for Older People, of the Parc Sanitari Pere Virgili; Complex Case Management, of the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona and the Promotion of Physical Activity, also of the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona.
ACT@Scale has developed a framework of assessment based on experience, practice and evidence using the Donabedian theoretical framework. To assess the implementation of the programmes, a collaborative methodology (Plan-Do-Study-Act) has been used. Thus, in order to assess processes of implementation and scalability, research has been done within four work packages:
- Service Selection, led by Kronikgune
- Business Models, led by the University of Groningen
- Citizen Empowerment, led by NIRE
- Change and Stakeholder Management, led by AQuAS
What have we learnt in relation to Change Management, Stakeholder and Staff Engagement?
- In relation to Stakeholder Management, the leaders of the programmes that completed the questionnaires agreed that participative and co-creation strategies need to be introduced to improve the quality of integrated care and to reduce the resistance of stakeholders to change, where all identified stakeholders feel part of the process.
- In terms of Change Management, regarding leadership, new communication strategies need to be incorporated which should be based on a collaborative methodology so as to detect and prioritise needs, implement them and monitor and assess them within the processes of change initiated.
- In terms of Staff Engagement, we can confirm that the implementation of programmes of integrated care is a dynamic process in which potential risks need to be identified and therefore, assessment and redesign need to be ongoing..
Integrated care contributes to the creation of new health scenarios, some in a state of change and others as yet unknown. These new scenarios should make us think about defining new professional profiles, new areas of expertise and identify new actors and “actresses”.

Post written by Núria Rodríguez-Valiente.